Phosphorus is the second most vital nutrient required by every existing live on the earth including plants and humans. It is structural element of the plants and humans DNA and RNA and it plays pivotal role such as cell division, and physiological responses. The deficiency of this nutrient may leads to serious problems like; apatite loss, bone pain in humans and growth stagnation in plants. Phosphorus, although is present in the earth in huge amount but not available for the plant and humans. The plant demand of phosphorus earlier fulfilled by using the chemically prepared phosphate fertilizers but its use generally has undesirable effect on the plants, humans and animals as well as environments. Phosphate solubilizing microorganisms under the natural and stressed conditions could be alternative and eco-friendly approach for agro-environmental sustainability. These microorganisms solubilizes inorganic and organic phosphorus both through various mechanism such as production of organic acids, inorganic acid, H2S, siderophores and protons; excretion of extracellular enzymes; direct oxidation pathway and enzymatic actions. Microorganisms with phosphate-solubilizing activity have been reported from different phyla of all three domain eukarya, archaea, and bacteria from various natural as well as stressful environmental conditions.
Phosphorus, the irreplaceable element is one of the most essential elements and a pillar of food security for every living cells or organism including microbe, plant, animals and humans [1]. It is structural element of RNA and DNA which plays diverse and significant role in the living organism. In plants, phosphorus plays important role in cell division, generation of energy, macromolecules biosynthesis, membrane integrity, photosynthesis, signal transduction, and plant respiration. In leguminous plants this element also helps in the fixing the nitrogen. On the other in humans phosphorus plays pivotal role in skeletal and non-skeletal tissues and it also act as signaling molecules which helps in inducing complex physiological responses [2]. Phosphorus deficiency often occurs in poor, weathering, and calcium carbonate-rich soils. In the case of human, due to phosphorus deficiency human suffer to loss of appetite, anxiety, bone pain, fragile bones, stiff joints, fatigue, irregular breathing, irritability, numbness, weakness, and weight change. In children, decreased growth and poor bone and tooth development may occur [3].
In soil, phosphorus accounts for 50 to 3000 mg kg−1, yet total P mineral available for plants uptake is 0.1%. Consequently, to fulfil the phosphorus demand of plant, huge amount of phosphatic fertilizers were being produced and used. The use of chemical phosphatic fertilizers over the long period of time has resulted in the precipitation of the fertilizer in the soil in huge proportion. With scientific advancements and modernization in agricultural practices, utilization of the agrochemicals to obtain high yield has been increasing over time. So, phosphatic fertilizers are also used in recommended doses to fulfil P requirement the demands. But, production of phosphatic fertilizers requires high cost and their excessive use is unsafe for the environment [4]. Therefore, researchers are focusing to find alternative and eco friendly strategies to deal with the problems of P availability and solubilization [5, 6]. The huge amount of fertilizer accumulation has resulted in the causing deleterious harm to animals, consumer health and soil fertility [7]. Phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms use as a bioinoculants is the sustainable and alternative approach that could help in achieving the same goal as chemical phosphatic fertilizers and phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms as bioinoculants in the fields could help in reducing the fertilizer input [8, 9].
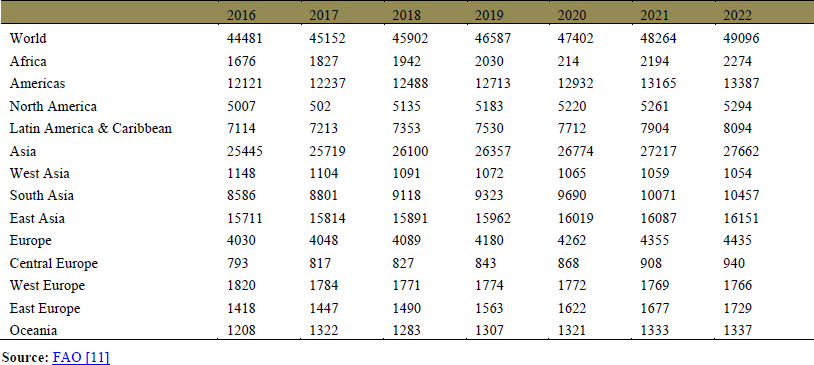 | Table 1: World phosphate fertilizer demand (thousand tonnes P2O5) forecast. [Click here to view] |
Phosphorus is mostly found in the atmosphere as small dust particles. In soil, phosphorus is present in the two forms i.e., 30-65% organic P (Inositol, phosphate, phospholipid and nucleic acid) and 35-75% inorganic P (Ca, Fe and Al phosphates). Phosphorus enters into soil through chemical fertilizers (inorganic sources), compost, biosolids, or dead plant or animal debris (organic sources), it cycles between several soil pools through the processes such as mineralization, immobilization, adsorption, precipitation, desorption, weathering, and dissolution [10]. Consequently, there has been an increase over the years in the demand for and use of phosphatic fertilizers to maintain a continuous supply of phosphorus in plants (Table 1) [11]. Humans have a substantial impact on the phosphorus cycle due to a variety of human activities, such as the use of chemical fertilizer, food distribution, and artificial eutrophication. Excessive use of these fertilizers reduces soil fertility and is harmful to soil microorganisms. When these flow into the surrounding water bodies, they pose a threat to the flora and fauna of the ecosystem. Thus, human activities tend to damage aquatic ecosystems whenever excess amounts of phosphorus are released into the water.
Phosphate solubilizing microorganisms solubilizes phosphorus for their own requirement and use which also fulfil the P mineral demand of the plants. Phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms disseminate phosphorus by three predominant ways i.e. mineralization, solubilizing and immobilization [12]. Phosphate solubilizing microorganism follows exhibits different mechanism for the solubilization of inorganic and organic phosphorus minerals present in soil (Figure 1). Inorganic phosphate including Fe-P, Ca-P and Al-P, solubilization is achieved by the microorganisms by mechanism such as production of organic acids, inorganic acid, H2S, siderophores and protons; excretion of extracellular enzymes; and direct oxidation pathway. On the other hand, the organic phosphate is solubilized via enzymatic action of non-specific acid phosphatases, C–P lyases, phytases, and phosphonatases. Phosphate solubilization through the organic acid productions is one of the most known mechanisms of soil and plant allied microorganisms. Microorganisms produced different types of organic acid namely, oxalic acid, tartaric acid, citric acid, gluconic acid and 2-ketogluconic acid. These organic acids helps in the cation and complexation of chelation and metal ions bound to phosphate, lowering of pH which avail the P for the uptake [13].
In the strategy of inorganic acid production, phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms produce acids like carbonic acid, nitric acid, sulfuric acid and hydrochloric acid, but these acids have low efficiency of P solubilization as compared to organic acid [14]. In the mechanism of proton extrusion from ammonium, phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms produce amino acids and which is assimilated by the ammonium ion present in soil that converted into ammonia. The excess of proton H+ present in the microbial cell is released into the cytoplasm. The ion released in soil lowers the pH and dissolute the insoluble phosphate [15]. Another mechanism of P-solubilization i.e. direct oxidation pathway releases inorganic P bound with Ca2+ and Fe2+. In this mechanism glucose is converted into gluconic acid in the presence of enzyme glucose dehydrogenase. The gluconic acid is further oxidized into 2-ketogluconic acid with help of gluconate dehydrogenase. The 2-ketogluconic acid act as chelators of Ca2+ and Fe2+ and which chelates them releases P mineral [16]. In the mechanism of EPS production, the microbial released EPS form the complex with metal ions and helps the release of P [16]. Mechanism of siderophores production helps in the release of P bound with Fe, as siderophores are the chelator of iron [17]. All these mechanism of phosphate solubilization is governed by the various sets of glucose dehydrogenase gene (gcd), pyrroloquinoline quinine (pqq A-F) genes and enolase gene (eno) [18].
 | Figure 1: Schematic presentation of phosphate solubilization by phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms and their role for agricultural sustainability [Click here to view] |
 | Figure 2: Number of research publications on phosphate solubilization [Source-PubMed]. [Click here to view] |
Phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms have been reported from various habitats and have capability to solubilize in stressful conditions including biotic and abiotic. Various microbes have been reported so far that have capability to solubilize P in the biotic and abiotic stressful conditions [19]. In a report, plant growth promoting bacteria Streptomyces was reported for solubilizing phosphorus under the biotic stress of panicle blight disease in rice plant [20]. Under the rain-fed conditions, Pseudomonas libanensis [21], Streptomyces laurentii, Penicillium sp. [22], and Acinetobacter calcoaceticus [23] was reported for solubilizing P mineral. In a report, Bacillus megaterium and B. subtilis was reported solubilizing phosphorus under salinity stress [24]. Heavy metal is also known as major abiotic stressor and microbes have also been reported for solubilizing phosphorus under heavy metal stressed conditions [25]. Phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms additionally possess other plant growth promoting capabilities. They enhance growth by producing plant growth regulators such as indole acetic acid, gibberellins and cytokinins; synthesizing siderophores, solubilizing K, Zn and Mn and showing bio-control activity against plant pathogens. Phosphate solubilizers also help the plant to withstand abiotic stress conditions of drought, salinity, high and low temperature, as well as heavy metal by synthesizing ACC deaminase and preventing oxidative damage [26]. Biofertilizers are living cells of plant associate and soil microorganisms that could be used in various types of bio-formulations. Biofertilizers come in two types of bioformulations i.e., liquid and powder, both of which are commercially available in the market. As a result, scientists and biofertilizer manufacturers must to work together to resolve bottlenecks in the bacterial bioformulation process [27]. There are huge and vast varieties of finding as phosphate solubilization for agricultural sustainability (Figure 2)
In conclusion, the scientific community is greatly focusing on more utilization of phosphate solubilizers with multifarious PGP attributes. Phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms can thus be utilized as bioinoculants to enhance the availability of P and to promote the growth of the plants and restore the fertility of the soil. It not only plays structural role in plant but also controls the metabolic functions of the plants. Phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms could be applied to crops to promote the growth or enhance P-availability simultaneously to reduce the dependence on chemical phosphatic fertilizers and restore soil fertility. Further understanding and study of genetics behind the phosphate solubilization would also be very beneficial. Lastly, the transfer of knowledge from the scientific community to farmers to appreciate and more utilization of bio based inoculants are of major importance.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
Author declares that there are no conflicts of interest.
REFERENCES
1. Yadav AN. Phytomicrobiomes for agro-environmental sustainability. J Appl Biol Biotechnol. 2021; 9(5):1-4. http://dx.doi.org/10.7324/JABB.2021.95ed
2. Bird RP and Eskin NAM. The emerging role of phosphorus in human health, in Advances in Food and Nutrition Research, N.A.M. Eskin, Editor. 2021, Academic Press. pp. 27-88. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.afnr.2021.02.001
3. Gupta U and Gupta S. Sources and deficiency diseases of mineral nutrients in human health and nutrition: a review. Pedosphere. 2014; 24(1):13-38. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(13)60077-6
4. Khan MS, Zaidi A, Wani PA. Role of phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms in sustainable agriculture-a review. Agron Sustain Dev. 2007; 27(1):29-43. https://doi.org/10.1051/agro:2006011
5. Verma P, Yadav AN, Khannam KS, Kumar S, Saxena AK, Suman A. Molecular diversity and multifarious plant growth promoting attributes of Bacilli associated with wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) rhizosphere from six diverse agro-ecological zones of India. J Basic Microbiol. 2016; 56(1):44-58. https://doi.org/10.1002/jobm.201500459
6. Yadav AN, Sachan SG, Verma P, Kaushik R, Saxena AK. Cold active hydrolytic enzymes production by psychrotrophic Bacilli isolated from three sub-glacial lakes of NW Indian Himalayas. J Basic Microbiol. 2016; 56:294-307. https://doi.org/10.1002/jobm.201500230
7. Rawat P, Das S, Shankhdhar D, Shankhdhar SC. Phosphate-Solubilizing Microorganisms: Mechanism and Their Role in Phosphate Solubilization and Uptake. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr. 2021; 21(1):49-68. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-020-00342-7
8. Kour D, Rana KL, Yadav AN, Sheikh I, Kumar V, Dhaliwal HS, Saxena AK. Amelioration of drought stress in Foxtail millet (Setaria italica L.) by P-solubilizing drought-tolerant microbes with multifarious plant growth promoting attributes. Environ Sustain. 2020; 3(1):23-34. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42398-020-00094-1
9. Kaur T, Devi R, Kour D, Yadav A, Yadav AN, Dikilitas M, Abdel-Azeem AM, Ahluwalia AS, Saxena AK. Plant growth promoting soil microbiomes and their potential implications for agricultural and environmental sustainability. Biologia. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-021-00806-w
10. Yadav AN, Kour D, Kaur T, Devi R, Yadav A, Dikilitas M, Abdel-Azeem AM, Ahluwalia AS, Saxena AK. Biodiversity, and biotechnological contribution of beneficial soil microbiomes for nutrient cycling, plant growth improvement and nutrient uptake. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol. 2021; 33:102009. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2021.102009
11. FAO, World fertilizer trends and outlook to 2022. http://www.fao.org/3/ca6746en/CA6746EN.pdf. 2019.
12. Kour D, Rana KL, Kaur T, Yadav N, Yadav AN, Kumar M, Kumar V, Dhaliwal HS, Saxena AK. Biodiversity, current developments and potential biotechnological applications of phosphorus-solubilizing and -mobilizing microbes: A review. Pedosphere. 2021; 31(1):43-75. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(20)60057-1
13. Kishore N, Pindi PK, Ram Reddy S. Phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms: a critical review. Plant Biol Biotechnol. 2015:307-333. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-81-322-2286-6_12
14. Yadav AN, Sharma D, Gulati S, Singh S, Dey R, Pal KK, Kaushik R, Saxena AK. Haloarchaea Endowed with Phosphorus Solubilization Attribute Implicated in Phosphorus Cycle. Sci Rep. 2015; 5(1):12293. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep12293
15. Gaind S. Phosphate dissolving fungi: mechanism and application in alleviation of salt stress in wheat. Microbiol Res. 2016; 193:94-102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2016.09.005
16. Krishnaraj P and Goldstein A. Cloning of a Serratia marcescens DNA fragment that induces quinoprotein glucose dehydrogenase-mediated gluconic acid production in Escherichia coli in the presence of stationary phase Serratia marcescens. FEMS Microbiol Let. 2001; 205(2):215-220. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.2001.tb10950.x
17. Birch L and Bachofen R. Complexing agents from microorganisms. Experientia. 1990; 46(8):827-834. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01935533
18. Kumar R and Shastri B, Role of phosphate-solubilising microorganisms in sustainable agricultural development, in Agro-Environmental Sustainability. 2017, Springer. p. 271-303. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-49724-2_13
19. Yadav AN. Biodiversity and bioprospecting of extremophilic microbiomes for agro-environmental sustainability. J Appl Biol Biotechnol. 2021; 9(3):1-6. https://doi.org/10.7324/JABB.2021.9301
20. Ngalimat MS, Mohd Hata E, Zulperi D, Ismail SI, Ismail MR, Mohd Zainudin NAI, Saidi NB, Yusof MT. Characterization of Streptomyces spp. from Rice Fields as a Potential Biocontrol Agent against Burkholderia glumae and Rice Plant Growth Promoter. Agronomy. 2021; 11(9):1850. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11091850
21. Kour D, Rana KL, Sheikh I, Kumar V, Yadav AN, Dhaliwal HS, Saxena AK. Alleviation of drought stress and plant growth promotion by Pseudomonas libanensis EU-LWNA-33, a drought-adaptive phosphorus-solubilizing bacterium. Proc Natl Acad Sci, India Sec B: Biol Sci. 2019:1-11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40011-019-01151-4
22. Kour D, Rana KL, Kaur T, Sheikh I, Yadav AN, Kumar V, Dhaliwal HS, Saxena AK. Microbe-mediated alleviation of drought stress and acquisition of phosphorus in great millet (Sorghum bicolour L.) by drought-adaptive and phosphorus-solubilizing microbes. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol. 2020; 23:101501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2020.101501
23. Yadav AN, Kour D, Ahluwalia AS. Soil and phytomicrobiomes for plant growth and soil fertility. Plant Sci Today. 2021; 8(sp1):1-5. https://doi.org/10.14719/pst.1523
24. Zhu Z, Zhang H, Leng J, Niu H, Chen X, Liu D, Chen Y, Gao N, Ying H. Isolation and characterization of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria and their effects on the growth of Medicago sativa L. under salinity conditions. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek. 2020; 113(9):1263-1278. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-020-01434-1
25. Kour D, Kaur T, Devi R, Yadav A, Singh M, Joshi D, Singh J, Suyal DC, Kumar A, Rajput VD, Yadav AN, Singh K, Singh J, Sayyed RZ, Arora NK, Saxena AK. Beneficial microbiomes for bioremediation of diverse contaminated environments for environmental sustainability: present status and future challenges. Environ Sci Poll Res. 2021; 28(20):24917-24939. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13252-7
26. Suyal DC, Joshi D, Kumar S, Bhatt P, Narayan A, Giri K, Singh M, Soni R, Kumar R, Yadav A, Devi R, Kaur T, Kour D, Yadav AN. Himalayan Microbiomes for Agro-Environmental Sustainability: Current Perspectives and Future Challenges. Microb Ecol. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-021-01849-x
27. Yadav AN. Beneficial plant-microbe interactions for agricultural sustainability. J Appl Biol Biotechnol. 2021; 9(1):1-4. https://doi.org/10.7324/JABB.2021.91ed